In all normal cases screening tests for colon and rectum cancer starts at the age of 50. Colorectal cancer is usually found after symptoms begin to appear at an advanced stage making screening all the more important. Early detection of colorectal cancer puts the patient at an advantage. In this article we discuss what can be done for screening and diagnosis of colorectal.
There are no specific known cause of most of the colorectal cancers and what makes things all the more tough for these type of cancers is that the symptoms start to appear when the disease is at an advanced stage. Let us start by looking at screening tests for colorectal cancer.
Screening Tests For Colon and Rectum Cancer
For screening of colorectal cancer one or more of the following tests may be prescribed:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: In case a person shows any signs and symptoms for colorectal cancer, the examining doctor will ask for complete medical history and make a physical examination to check for symptoms and risk factors. The doctor will examine the abdominal area and the other parts of the body. A DRE (Digital Rectal Examination) may also be performed. This requires a lubricated, gloved finger to inserted into the rectum to feel for abnormalities.
- FOBT: Fecal Occult Blood Test: The test aims at checking for traces of blood in the fecal material. There are two types of tests in this specific category – guaiac FOBT and immunochemical FOBT. In the first type chemical guaiac is used for detecting any traces of Heme, the component that contains iron in the blood; the second type uses antibodies for detecting human hemoglobin protein in stool. Stool samples are collected over 1 to 3 movements. The test should be performed every 1 to 2 years for people over the age of 50.
- Sigmoidoscopy: The test involves examining the rectum and the lower colon with a lighted instrument known by the name sigmoidoscope. Unwanted growth (precancerous and cancerous) can be found and removed. The test requires thorough cleansing of the colon before the test can be done.
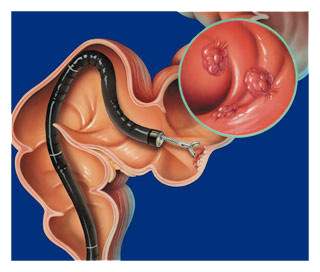
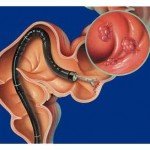
- Colonoscopy: This test involves examination of the rectum and the complete colon are examined using a lighted instrument known by the name colonoscope. Just as the earlier test, it can be used for detecting and removing growths. The test requires thorough cleansing of the colon before the test can be done.
- Virtual Colonoscopy: For this test a special x-ray equipment is used for producing images of the rectum and the colon. A computer is used for assembling the images. The test is less invasive in nature, does not require sedation and as a result causes less discomfort.
- Double Contrast Barium Enema (DCBE): A series of x-rays of the complete colon and rectum are taken after the patient is given an enema with a barium solution. This test allows imaging of small polyps that may be missed.
Screening methods for colorectal cancer are still being studied. Studies are being undertaken in order to determine the risks associated with these tests.










